Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Epidemiol Health > Volume 40; 2018 > Article
-
Original Article
The association between aggression and risk of Internet gaming disorder in Korean adolescents: the mediation effect of father-adolescent communication style -
Eunjin Kim1
 , Hyeon Woo Yim1
, Hyeon Woo Yim1 , Hyunsuk Jeong1
, Hyunsuk Jeong1 , Sun-Jin Jo1
, Sun-Jin Jo1 , Hae Kook Lee2
, Hae Kook Lee2 , Hye Jung Son1
, Hye Jung Son1 , Hyun-ho Han1
, Hyun-ho Han1
-
Epidemiol Health 2018;40:e2018039.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2018039
Published online: August 8, 2018
1Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- Correspondence: Hyeon Woo Yim Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 222 Banpo-daero, Seocho-gu, Seoul 06591, Korea E-mail: y1693@catholic.ac.kr
©2018, Korean Society of Epidemiology
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
OBJECTIVES
- Open and supportive communication between parents and children is known to reduce adolescents’ delinquent behavior. Recently, the risk of Internet gaming disorder (IGD) has been increasing in adolescents. The purpose of this study was to investigate the mediating effects of parent-child communication styles on the relationship between adolescent aggressiveness and risk of IGD.
-
METHODS
- Participants in this study were 402 first-year students from 4 middle schools in Seoul who enrolled in the Internet user Cohort for Unbiased Recognition of gaming disorder in Early adolescence (iCURE) and completed baseline assessment in 2016. The structural equation model was constructed based on an aggression questionnaire, the Internet game use-elicited symptom screen, a mother-child communication inventory, and a father-child communication inventory.
-
RESULTS
- Adolescents’ aggressiveness was found to be related to their risk of IGD. The father-child communication style mediated the relationship between aggression and risk of IGD. However, the mother-child communication style had no mediating effect.
-
CONCLUSIONS
- Our findings suggest that fathers should make an effort to improve open and positive communication skills with their children, because the father-child communication style plays an important role in the relationship between adolescent aggressiveness and risk of IGD.
- During the stormy period of adolescence, teenagers undergo development to adulthood and begin to exhibit problematic behaviors or negative emotions. In adolescents, prefrontal development is still incomplete, and the amygdala, which controls fear and anger, plays a larger role in behavior; therefore, adolescents are more prone to exhibiting impulsive behaviors. In addition, adolescents’ bodies release testosterone, the male hormone, greater than are released during the juvenile period, and this hormone stimulates their aggression and anger to make them more aggressive [1]. Aggression is an intended behavior that harms or hurts others and includes the angry emotions that lead to aggressive behaviors [2].
- Aggression increases during adolescence and then consistently decreases as one enters adulthood [3]. Aggression during adolescence has been reported to be associated with antisocial behaviors such as delinquency, addiction, and violence as well as with crime and school maladjustment. Families affect adolescents’ socialization and can thus play an important role in adolescents’ antisocial and criminal behaviors. Parents play the most important role in adolescents’ process of socialization [4]. Communication between adolescents and parents is known to be positively associated with adolescents’ achievement [5], self-esteem [6], and psychological health [7], and negatively associated with loneliness, depression [6], drug abuse, and delinquent behaviors [8]. Open and free parent-child communication helps prevent delinquent behaviors, whereas closed and repressive communication negatively affects the child and leads to delinquency [9].
- Owing to the rapid development of information and communication technology in recent years, Internet games have become popular through high-speed Internet. Internet games have become a part of leisure activities enjoyed by children and adults, but addiction to Internet games can lead to a variety of social, physical, and psychological problems [10]. One study has shown that Internet gaming disorder (IGD) causes the same brain changes as those caused by alcohol and drug addiction [11]. The frontal lobe plays the most important role in self-recognition, behavior planning, information integration, and storing of emotions, impulses, and desire. It slowly develops between 12 and 20 years of age at the latest; thus, such brain changes affect adolescents more than they affect adults [12].
- Middle school students are the most frequent users of Internet games. A survey of overdependence on the Internet has shown that adolescents occupy the highest proportion (30.6%) of the high-risk overdependence group among all age groups [13]. The risk factors of IGD that have been identified to date include stress, depression, anxiety, impulsiveness, aggression, and financial status. Of these, aggression is known as one of the causes of IGD [14-16].
- Thus, this study was conducted to investigate whether or not open and free parent-child communication has a mediating effect on the risk of IGD among adolescents, since parents play a mediating role in adolescents’ delinquent and violent behaviors.
INTRODUCTION
- Subjects
- The Internet user Cohort for Unbiased Recognition of gaming disorder in Early Adolescence (iCURE) was established to investigate the characteristic of IGD and observe the natural progress of IGD among third and fourth graders in primary school and first-year students in middle school residing in Seoul and Gyeonggi Province [17]. This study included 440 first graders in 4 middle schools located in Seoul that were surveyed between April 6 and May 26, 2016, during the iCURE cohort research. All 4 schools were coeducational.
- A structural equation model was analyzed to answer the research question. For the sample size of the structural equation model, 10-20 subjects are needed for the estimation of each parameter [18]. In this study, 20 parameters were to be estimated using a model constructed with 4 measurements, and thus a sample size of over 400 was planned.
- Baseline data about aggression, risk of IGD, and mother- and 2father-child communication styles were extracted from the iCURE cohort data and analyzed. Thirty-eight cases with missing data due to the absence of a mother or father were excluded, and the data of 402 subjects were finally used.
- Ethics statements
- This study extracted and analyzed data from the iCURE cohort study and was approved by the institutional review board of the Catholic University of Korea (no. MC17EESI0073).
- Methods of investigation and tools
- A web-based self-reported survey was conducted during school hours. The following tools were used.
- The Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire (AQ) was used to investigate aggression [19]. This scale consists of 27 questions and 4 dimensions of aggression (physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger, and hostility). It is a 5-point Likert scale with scores ranging from 1 (never) to 5 points (very true). Total scores ranged from 27 to 135 points, with higher scores indicating higher levels of aggression. In this study, the internal consistency of this tool (Cronbach‘s α) was 0.88. The Korean version of the AQ was used in this study [20].
- The Internet Game Use-Elicited Symptom Screen (IGUESS) was used to measure the risk of IGD. The IGUESS is a self-reported scale used to screen symptoms of IGD based on the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) suggested IGD diagnostic criteria. It consists of nine questions rated on a 4-point Likert scale, with total scores ranging from 0 to 27 points. Higher scores indicate a higher risk of IGD. In this study, the internal consistency (Cronbach‘s α) of this tool was 0.86 [21].
- The Parent-Adolescent Communication Inventory (PACI) developed by Barnes & Olson [22] was used to assess the style of parent-child communication. The tool consists of 20 questions with two types of communication: open communication and problematic communication. The questions are rated on a 5-point Likert scale with scores ranging from 1 (never) to 5 points (very true) for each question. Total scores range from 20 to 100 points, with higher scores indicating more open and positive communication and lower scores indicating more dysfunctional and negative communication. The internal consistency of this tool (Cronbach‘s α) was 0.91 in this study. The Korean version of the tool was used in this study [23].
- Statistical analysis
- SPSS version 24 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used for descriptive statistics and correlational analysis. AMOS version 23 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used to analyze the measurement model and mediating effects using structural equation modeling. The research model was constructed based on the assumption that the style of father- or mother-child communication is a major mediating variable in the relationship between aggression and risk of IGD. IGUESS scores, which were one of the major variables, were found not to have a normal distribution in the normality test and were converted to log values. A correlational analysis was performed to analyze the correlations between aggression, risk of IGD, and style of mother- or father-child communication included in the research model and to check for multicollinearity. A confirmatory factor analysis, which is used to confirm inherent factor dimensions and hypotheses based on the researcher’s knowledge and to test the validity of measurement scales for a certain concept, was performed to evaluate the validity of each measurement parameter.
- The construct validity of the major variables was tested in terms of convergent validity and discriminant validity. Convergent validity is the degree to which two or more measurement parameters correlate with one another with respect to a construct. A standardized factor loading of 0.5 is essential and one of 0.7 or higher is advisable. Average variance extracted (AVE) is the ratio of the sum of the squares of the factor loadings and that sum plus the sum of the factor error variances. In general, a model is deemed to have convergent validity when its AVE is 0.5 or over. This means that half of all variance must be explained by the construct in order to accept the parameters.
- The validity of a structural equation model is determined by assessing the consistency between the research model and the actual covariance data and how fit the covariance structural model is for the assumption. In this study, the structural equation model was deemed fit under the conditions of a normed χ2, which is an absolute fit index that represents how well a research model reflects the enrolled data, of 3 or less; a goodness of fit index (GFI) of 0.90 or over; a root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) of 0.05 or less; a comparative fit index (CFI), which determines how fit a model is in comparison with a null model in which no relationships are set between all variables of a model, of 0.9 or over; and a Tucker-Lewis index (TLI) of 0.9 or over.
- To test the statistical significance of indirect effects, a bootstrap method was used in which 20,000 data samples randomly sampled from the original data were used for parameter estimation and 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Aggression
Risk of Internet gaming disorder
Style of parent-child communication
- General characteristics
- First-year 4 coeducational middle school students were included. Of the students, 223 (55.5%) were male. The mean aggression score was 57.4±15.0 points, the mean PACI score for father-child communication was 69.8±15.1 points, and that for mother-child communication was 63.0±13.2 points. On IGD risk scores, 77.8% had scores of 0-5 points, 13.2% scores of 6-9 points, and 9.0% scores of 10 points or over, which is the cut-off point of the IGD (Table 1).
- Correlational analysis
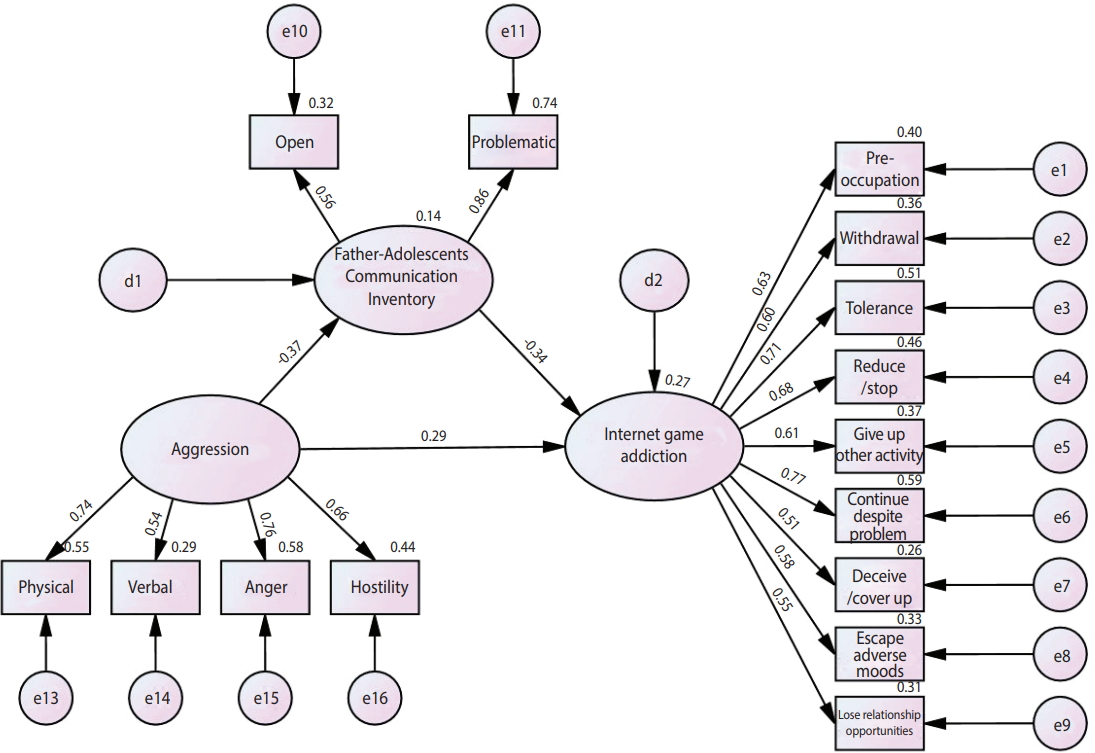
- A correlation analysis of the major measurement parameters included in the research models (aggression, risk of IGD, and styles of father- and mother-child communication) showed a significantly positive correlation between aggression and the risk of IGD (r=0.32, p<0.001). Aggression was significantly negatively correlated with styles of father-child communication (r=-0.22, p<0.001), and styles of father-child communication were significantly negatively correlated with the risk of IGD (r=-0.38, p<0.001). Styles of mother-child communication did not significantly correlate with aggression (r=0.04, p=0.39), styles of father-child communication (r=0.03, p=0.61), or the risk of IGD (r=-0.05, p=0.30) (Table 2). Thus, a model was constructed with styles of father-child communication as a mediating factor in the relationship between aggression and the risk of IGD (Figure 1).
- Evaluation of measurement models
- Confirmatory factor analysis yielded a construct reliability, which measures convergent validity, of 0.94 for IGD, 0.71 for styles of father-child communication, and 0.87 for aggression; these values satisfied the acceptable standard value of 0.7 or above. The mean AVE was 0.65 for IGD, 0.57 for styles of father-child communication, and 0.63 for aggression; these values satisfied the acceptable standard value of 0.5 or above, meaning that the model had convergent validity (Figure 1).
- Regarding the discriminant validity of the major measurement parameters, the parameters had a mean AVE value greater than the square of their correlation coefficient below the diagonal on Table 3 and thus had discriminant validity (Table 3).
- Based on the results of a goodness of fit test of the model with styles of father-child communication as a mediating factor in the relationship between aggression and IGD, the mediating effect and the model were deemed fit (χ2=201.52, df=87.00, χ2/df =2.32, GFI=0.94, RMSEA=0.06, CFI=0.94, TLI=0.92) (Table 4).
- Analysis of the structural equation model showed that the direct effect of aggression on IGD was 0.29 and was statistically significant (p<0.001). The indirect effect of styles of father-child communication in the relationship between aggression and the risk of IGD was 0.13. The significance of indirect effects was tested using the bootstrap method, and the path through which styles of father-child mediated the relationship between aggression and the risk of IGD was statistically significant (p<0.001). Thus, it was found that styles of father-child communication partially mediated the effect of aggression on the risk of IGD, and their total effect was found to be 0.42 (p<0.001) (Table 5).
RESULTS
Confirmatory factor analysis
Structural equation model goodness of fit test
Direct, indirect and total effects
- The mean aggression score measured by the AQ developed by Buss & Perry [19] was 57.34±15.00, which is somewhat lower than scores observed in previous studies [24]. The AQ defines aggression as the tendency to harm or hurt others, and aggression includes physical and verbal aggression toward others and dangerous ways of thinking and emotions. This reflects the impulsiveness or aggressive desire that adolescents experience during the process of adjusting to hormonal and environmental changes in the transitional period. The subjects in this study were first-year students in middle school. Assuming that they had not reached the peak of puberty, it is reasonable to argue that they had lower aggression scores than subjects in other studies that included the entire population of middle school students or included high school students. In a cohort study that included 5,151 adolescents aged 11-18, physical aggression reached a peak before and after the age of 15 years, and social aggression reached a peak before and after the age of 14. Adolescents tended to show low levels of aggression in early adolescence that gradually increased and then decreased with age [25].
- Biological factors have been reported to affect aggression more significantly than environmental factors [26]. Brain imaging results have shown that aggression is associated with a reduced volume of gray matter in the medial prefrontal cortex and lateral frontal cortex. Reduced gray matter in the prefrontal region is associated with aggressive behaviors regardless of diagnosis of psychological disorder, and this suggests that aggression is affected by biological factors since many genetic factors come into play in the gray matter of the frontal cortex [27]. A long-term twin follow-up study showed that genetic factors play a major role in social aggression [28,29].
- The DSM-5 diagnoses IGD when at least five of nine symptoms are observed. The score range for the IGUESS is 0-27 points with a cut-off point for the risk of IGD of 10 points or greater. In the IGUESS, two points are given for symptoms that occur “frequently.” Scores of 10 points or greater thus correspond to displaying five of the nine symptoms in the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for IGD [21]. In this study, 9.0% of all subjects had the cut-off score of 10 points or greater.
- A significant association was found between aggression during adolescence and the risk of IGD (r=0.32, p<0.001). This finding was consistent with a previous report that aggression affects the risk of IGD [30-32]. Thus, higher levels of aggression during adolescence indicate a higher likelihood of being included in the high-risk group for IGD.
- This study investigated whether or not styles of parent-child communication can decrease the risk of IGD in the relationship between aggression and the risk of IGD and found that styles of mother-child communication had no mediating effects on the relationship between aggression and the risk of IGD, whereas styles of father-child communication did.
- Analysis of the structural equation model showed that the total effect of aggression on the risk of IGD was 0.42, of which 0.29 was the direct effect and 0.13 was an indirect effect mediated by father-child communication. Standardized path coefficients of 0.1-0.3 indicate small effects, those of 0.3-0.5 medium effects, and those of 0.5 or greater large effects. Thus, father-child communication can be considered as having a medium to large effect on the association between adolescents’ aggression and the risk of IGD. Prospective randomized clinical trials are needed to investigate whether encouraging open parent-child communication contributes to reducing problematic behaviors including IGD.
- Communication is a complex and dynamic interactive process. According to a theory comparing parental roles, in a traditional family the father plays an “instrumental role” as the family’s representative, whereas the mother plays an “expressive role” of satisfying emotional needs. During the process of raising children, the father plays a controlling role in his children’s behaviors, and the mother plays a nurturing role by providing affection through words, behavior, and physical contact. When playing with his/her father, a child can learn that physical violence such as kicking and biting is not socially acceptable as well as learn the proper balance between timidity and aggression [33]. Considering that parents have different impacts on their children depending on their genders, the risk of IGD may be more associated with fathers. In a British cohort follow-up study, fathers’ involvement and attitude in early adolescence had an important impact on children’s psychological health [34]. Although it is generally known that mothers have a significant impact on their children, the reason that fathers had a greater impact on the association between aggression and the risk of IGD may be that the study participants were in the first year of middle school. Further research is necessary to determine whether the results of this study are phenomena that occur during a specific period or throughout adolescence.
- The effect of environmental factors on aggression varies depending on gender, with females affected relatively less by the environment [29]. To investigate the differences in the mediating effect of father-child communication on the association between aggression and the risk of IGD, a multi group structural equation model stratified by gender was analyzed. No sex differences were found, and styles of father-child communication were identified as a mediating factor for both males and females (results not provided).
- This study has several limitations. First, since it is a cross-sectional study, it cannot analyze the chronological relationship between adolescents’ aggression, styles of parent-child communication, and IGD. Longitudinal studies must be conducted to understand the causal relationships between these variables.
- Second, there is a possibility of misclassification since the diagnostic criteria for IGD have not been clearly established. However, the IGUESS, which classifies risk of IGD under conditions for further study in DSM-5, was used to increase the reliability and validity of such tests. Since the IGUESS is based on self-reported responses, the possibility of false positives and false negatives cannot be eliminated.
- Third, the results of this study are based on subjects from four middle schools in Seoul who were selected by convenience sampling, and since the subjects were in their first year of middle school, the results cannot be generalized to the entire population of middle school students.
- Previous studies evaluated the combined effects of parent-child communication styles in mediating effect on relationship between aggression and gaming addiction. However, we distinguished between mothers and fathers in parent-child communication to analyze the mediation effect using a structural equation model.
- In this study, aggression during adolescence was associated with the risk of IGD. The mediating effect of father-adolescent communication observed in this study suggests that efforts for open and positive communication between fathers and adolescents are necessary.
DISCUSSION
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Mean | Standard deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Aggression | 1.00 | 57.34 | 15.00 | |||
| 2. Father-adolescent communication style | -0.22*** | 1.00 | 69.80 | 15.06 | ||
| 3. Mother-adolescent communication style | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 63.01 | 13.15 | |
| 4. Risk of Internet game disorder | 0.32*** | -0.38*** | -0.05 | 1.00 | 3.61 | 4.00 |
| Aggression | Father-adolescent communication style | Risk of Internet game disorder | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggression | 0.63 | ||
| Father-adolescent communication style | 0.05 | 0.57 | |
| Risk of Internet game disorder | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.65 |
| Index | χ2 | df | χ2/df | GFI | RMSEA | CFI | TLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The mediation model | 201.52 | 87.00 | 2.32 | 0.94 | 0.06 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| Path |
Effect*** |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Direct | Indirect | |
| Aggression → risk of IGD | 0.42 | 0.29 | 0.13 |
- 1. Duke SA, Balzer BW, Steinbeck KS. Testosterone and its effects on human male adolescent mood and behavior: a systematic review. J Adolesc Health 2014;55:315-322.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Orpinas P, Frankowski R. The aggression scale: a self-report measure of aggressive behavior for young adolescents. J Early Adolesc 2001;21:50-67.Article
- 3. Liu J, Lewis G, Evans L. Understanding aggressive behaviour across the lifespan. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs 2013;20:156-168.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Granic I, Dishion TJ, Hollenstein T. The family ecology of adolescence: a dynamic systems perspective on normative development. In: Adams GR, Berzonsky MD, eds. Blackwell handbook of adolescence. Oxford: Blackwell; 2003. p 60-91.
- 5. Cheung CS, Pomerantz EM. Why does parents’ involvement enhance children’s achievement? The role of parent-oriented motivation. J Educ Psychol 2012;104:820-832.Article
- 6. Cava MJ, Buelga S, Musitu G. Parental communication and life satisfaction in adolescence. Span J Psychol 2014;17:E98.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Collins WE, Newman BM, McKenry PC. Intrapsychic and interpersonal factors related to adolescent psychological well-being in stepmother and stepfather families. J Fam Psychol 1995;9:433-445.ArticlePDF
- 8. Luk JW, Farhat T, Iannotti RJ, Simons-Morton BG. Parent-child communication and substance use among adolescents: do father and mother communication play a different role for sons and daughters? Addict Behav 2010;35:426-431.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Khaokhajorn P, Samipak S, Nithithanasilp S, Tanticharoen M, Amnuaykanjanasin A. Production and secretion of naphthoquinones is mediated by the MFS transporter MFS1 in the entomopathogenic fungus Ophiocordyceps sp. BCC1869. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2015;31:1543-1554.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Brooks F, Magnusson J, Klemera E, Chester K, Spencer N, Smeeton N. HBSC England National Report: health behaviour in school-aged children (HBSC): World Health Organization collaborative cross national study; 2015 [cited 2018 Aug 29]. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282857316_HBSC_England_National_Report-2015
- 11. Lin F, Zhou Y, Du Y, Qin L, Zhao Z, Xu J, et al. Abnormal white matter integrity in adolescents with internet addiction disorder: a tract-based spatial statistics study. PLoS One 2012;7:e30253.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Arain M, Haque M, Johal L, Mathur P, Nel W, Rais A, et al. Maturation of the adolescent brain. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2013;9:449-461.PubMedPMC
- 13. Ministry of Science and ICT. Survey on the Internet usage; 2017 [cited 2018 Sep 13]. Available from: https://www.msit.go.kr/web/msipContents/contentsView.do?cateId=mssw11241&artId=1360419 (Korean)
- 14. Gunuc S. Peer influence in Internet and digital game addicted adolescents: is Internet/digital game addiction contagious? Int J High Risk Behav Addict 2017;6:e33681.Article
- 15. Kuss DJ. Internet gaming addiction: current perspectives. Psychol Res Behav Manag 2013;6:125-137.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Kuss DJ, Lopez-Fernandez O. Internet addiction and problematic Internet use: a systematic review of clinical research. World J Psychiatry 2016;6:143-176.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Jeong H, Yim HW, Jo SJ, Lee SY, Kim E, Son HJ, et al. Study protocol of the Internet user Cohort for Unbiased Recognition of gaming disorder in Early adolescence (iCURE), Korea, 2015-2019. BMJ Open 2017;7:e018350.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Wolf EJ, Harrington KM, Clark SL, Miller MW. Sample size requirements for structural equation models: an evaluation of power, bias, and solution propriety. Educ Psychol Meas 2013;76:913-934.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Buss AH, Perry M. The aggression questionnaire. J Pers Soc Psychol 1992;63:452-459.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Seo S, Kwon S. Validation study of the Korean version of the aggression questionnaire. Korean J Clin Psychol 2002;21:487-501. (Korean).
- 21. Jo SJ, Yim HW, Lee HK, Lee HC, Choi JS, Baek KY. The Internet Game Use-Elicited Symptom Screen proved to be a valid tool for adolescents aged 10-19 years. Acta Paediatr 2018;107:511-516.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Barnes HL, Olson DH. Parent-adolescent communication scale. In: Olson DH, ed. Family inventories: inventories used in a national survey of families across the family life cycle. St. Paul: University of Minnesota; 1982. p 33-48.
- 23. Min H. Circumplex model and parent-child communication. [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University; 1990. (Korean).
- 24. Moon JY, Kim SW, Lee KE, Gwak HS. Correlation between aggression and health behaviors of Korean high school students. Korean J Clin Pharm 2014;24:144-153. (Korean).
- 25. Karriker-Jaffe KJ, Foshee VA, Ennett ST, Suchindran C. The development of aggression during adolescence: sex differences in trajectories of physical and social aggression among youth in rural areas. J Abnorm Child Psychol 2008;36:1227-1236.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Niv S, Tuvblad C, Raine A, Baker LA. Aggression and rule-breaking: heritability and stability of antisocial behavior problems in childhood and adolescence. J Crim Justice 2013;41:285-291.Article
- 27. Coccaro EF, Cremers H, Fanning J, Nosal E, Lee R, Keedy S, et al. Reduced frontal grey matter, life history of aggression, and underlying genetic influence. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 2018;271:126-134.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Porsch RM, Middeldorp CM, Cherny SS, Krapohl E, van Beijsterveldt CE, Loukola A, et al. Longitudinal heritability of childhood aggression. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2016;171:697-707.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Slawinski BL, Klump KL, Burt SA. The etiology of social aggression: a nuclear twin family study. Psychol Med. 2018 doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291718000697Article
- 30. Grüsser SM, Thalemann R, Griffiths MD. Excessive computer game playing: evidence for addiction and aggression? Cyberpsychol Behav 2007;10:290-292.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Lim J. The mediation model verification of private self-consciousness on game addiction and aggression. J Korea Contents Assoc 2016;4:250-261. (Korean).Article
- 32. Lee J, Choi KS. Longitudinal structural equation modeling of internet game and aggression in children. Open J Nurs 2015;5:426-436.Article
- 33. Yogman M, Garfield CF; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health. Fathers’ roles in the care and development of their children: the role of pediatricians. Pediatrics 2016;138:e20161128.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Opondo C, Redshaw M, Quigley MA. Association between father involvement and attitudes in early child-rearing and depressive symptoms in the pre-adolescent period in a UK birth cohort. J Affect Disord 2017;221:115-122.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Childhood harsh discipline and behavioral problems: The mediating roles of attachment dimensions
Ying Qing Won, Yena Kyeong, Peipei Setoh
Child Protection and Practice.2025; 5: 100129. CrossRef - Internet gaming disorder in children and adolescents: A systematic review of familial protective and risk factors
Teodora-Carina Petrescu, Agata Błachnio, Violeta Enea
Addictive Behaviors.2025; 167: 108345. CrossRef - Religious Iconography in Digital Media: Analyzing its Influence on the Untouchable Society
Wahyu Ilaihi, Ali Nurdin
KOMUNIKA: Jurnal Dakwah dan Komunikasi.2025; 19(1): 59. CrossRef - A systematic review of the association between parent‐child communication and adolescent mental health
Holger Zapf, Johannes Boettcher, Yngvild Haukeland, Stian Orm, Sarah Coslar, Krister Fjermestad
JCPP Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological distress and aggression among adolescents with internet gaming disorder symptoms
Xi Deng, Yu-Bo Hu, Chun-Yan Liu, Qi Li, Ning Yang, Qi-Yu Zhang, Lu Liu, Jian-Ni Qiu, Hong-Bin Xu, Li Xue, Yan-Wei Shi, Xiao-Guang Wang, Hu Zhao
Psychiatry Research.2024; 331: 115624. CrossRef - The role of self-esteem in triggering and maintaining gaming for people with gaming disorder cut-off scores and above average gaming disorder scores: A quasi-experimental study
Michael Kavanagh, Charlotte Brett, Catherine Brignell
Computers in Human Behavior.2024; 152: 108051. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the gaming disorder scale for adolescents (GADIS-A)
Öznur Başdaş, Harun Özbey, Meral Bayat
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 77: e218. CrossRef - Perceived parental psychological control and the risk of internet gaming disorder in adolescents: a cross-sectional study
Nazan Turan, Afra Alkan, Yasemin Çekiç
Current Psychology.2024; 43(25): 21735. CrossRef - Association Between Mental Health Problems and Internet Gaming Disorder Using Clinical Diagnostic Interviews: A Two-Year School-Based Longitudinal Study
Hyunsuk Jeong, Hyeon Woo Yim, Marc N. Potenza, Seung-Yup Lee, Misun Park
International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting Smartphone Addiction Trajectories in Korean Adolescents: A Longitudinal Analysis of Protective and Risk Factors Based on a National Survey from 2018 to 2020
Kyung-Yi Do, Chun-Bae Kim
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2024; 36(6-7): 550. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Parent–Child Communication Measures: Instruments and Their Psychometric Properties
Holger Zapf, Johannes Boettcher, Yngvild Haukeland, Stian Orm, Sarah Coslar, Silke Wiegand-Grefe, Krister Fjermestad
Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review.2023; 26(1): 121. CrossRef - Parental behaviors associated with internet gaming disorder in children and adolescents: A quantitative meta-analysis
Iulia Maria Coşa, Anca Dobrean, Raluca Diana Georgescu, Costina Ruxandra Păsărelu
Current Psychology.2023; 42(22): 19401. CrossRef - Effective interventions for gaming disorder: A systematic review of randomized control trials
Yuzhou Chen, Jiangmiao Lu, Ling Wang, Xuemei Gao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Internet gaming disorder and aggression: A meta-analysis of teenagers and young adults
Shunyu Li, Zhili Wu, Yuxuan Zhang, Mengmeng Xu, Xiaotong Wang, Xiaonan Ma
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship of Gaming Disorder with parenting based on low affection-communication and personality trait of neuroticism in adolescents
Francesc Rodríguez-Ruiz, María Isabel Marí-Sanmillán, Ana Benito, Francisca Castellano-García, Marta Sánchez-Llorens, Isabel Almodóvar-Fernández, Gonzalo Haro
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation Between Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Internet Gaming Disorder or Gaming Disorder
Ji Sun Hong, Sujin Bae, Vladan Starcervic, Doug Hyun Han
Journal of Attention Disorders.2023; 27(11): 1252. CrossRef - Cognitive emotion regulation mediates the relationship between big-five personality traits and internet use disorder tendencies
Jafar Hasani, Seyed Javad Emadi Chashmi, Mahsa Akbarian Firoozabadi, Leila Noory, Ofir Turel, Christian Montag
Computers in Human Behavior.2023; : 108020. CrossRef - Attention Circuits Mediate the Connection between Emotional Experience and Expression within the Emotional Circuit
Na Rae Won, Young-Don Son, Sun Mi Kim, Sujin Bae, Jeong Hee Kim, Jong-Hoon Kim, Doug Hyun Han
Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience.2023; 21(4): 715. CrossRef - The relationship between dissociation symptoms, sleep disturbances, problematic internet use and online gaming in adolescents
Ummugulsum Gundogdu, Mehtap Eroglu
Psychology, Health & Medicine.2022; 27(3): 686. CrossRef - Developmental Assets, Self-Control and Internet Gaming Disorder in Adolescence: Testing a Moderated Mediation Model in a Longitudinal Study
Guo-Xing Xiang, Xiong Gan, Xin Jin, Yan-Hong Zhang, Cong-Shu Zhu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Online gaming addiction in youth: Some comments on Rosendo-Rios et al. (2022)
Mark D. Griffiths
Addictive Behaviors.2022; 130: 107311. CrossRef - Advanced Concepts of the Role of Social Factors in the Development of Internet Addiction Behavior in Children and Adolescents (Based on Foreign Studies)
N.B. Semenova
Social Psychology and Society.2022; 13(1): 22. CrossRef - Correlations Between Psychological Status and Perception of Facial Expression
Sujin Bae, Eunhee Rhee, Beom Seuk Hwang, Young Don Son, Ji Hyun Bae, Doug Hyun Han
Psychiatry Investigation.2022; 19(6): 435. CrossRef - Do Individuals with Internet Gaming Disorder Share Personality Traits with Substance-Dependent Individuals?
Julie Giustiniani, Magali Nicolier, Madeline Pascard, Caroline Masse, Pierre Vandel, Djamila Bennabi, Sophia Achab, Frédéric Mauny, Emmanuel Haffen
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(15): 9536. CrossRef - Associations of Adolescents’ Excessive Electronic Device Use, Emotional Symptoms, Sleep Difficulty, and Communication with Parents: Two-wave Comparison in the Czech Republic
Yi Huang, Jinjin Lu
Children.2022; 9(8): 1186. CrossRef - “Game (not) Over”: A Systematic Review of Video Game Disorder in Adolescents
Claudio Rojas-Jara, Roberto Polanco-Carrasco, Rocío Navarro-Castillo, Francisca Faúndez-Castillo, Matías Chamorro-Gallardo
Revista Colombiana de Psicología.2022; 31(2): 45. CrossRef - The association between parent-child relationship and problematic internet use among English- and Chinese-language studies: A meta-analysis
Yalin Zhu, Linyuan Deng, Kun Wan
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The directionality of anxiety and gaming disorder: An exploratory analysis of longitudinal data from an Australian youth population
Seungyeon Kim, Katrina E. Champion, Lauren A. Gardner, Maree Teesson, Nicola C. Newton, Sally M. Gainsbury
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influences of Emotional Information on Response Inhibition in Gaming Disorder: Behavioral and ERP Evidence from Go/Nogo Task
Yuzhou Chen, Hongling Yu, Xuemei Gao
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 16264. CrossRef - Global prevalence of gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Matthew WR Stevens, Diana Dorstyn, Paul H Delfabbro, Daniel L King
Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry.2021; 55(6): 553. CrossRef - Exploring the Influence of Parenting Style on Adolescents’ Maladaptive Game Use through Aggression and Self-Control
Hyeon Gyu Jeon, Sung Je Lee, Jeong Ae Kim, Gyoung Mo Kim, Eui Jun Jeong
Sustainability.2021; 13(8): 4589. CrossRef - Developmental pathways from parental rejection to adolescent internet gaming disorder: A parallel process latent growth model
Jianjun Zhu, Yuanyuan Chen
Children and Youth Services Review.2021; 128: 106128. CrossRef - Internet Gaming Disorder in adolescence: investigating profiles and associated risk factors
Mirna Macur, Halley M. Pontes
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability, and Convergent and Discriminant Validity of Gaming Disorder Scales: A Meta-Analysis
Seowon Yoon, Yeji Yang, Eunbin Ro, Woo-Young Ahn, Jueun Kim, Suk-Ho Shin, Jeanyung Chey, Kee-Hong Choi
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of deliberate self-harm among adolescents: Answers from a cross-sectional study on India
Debashree Sinha, Shobhit Srivastava, Prem Shankar Mishra, Pradeep Kumar
BMC Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Gaming disorder and bidirectional relationships with aggression and impulsivity
Hyunsuk Jeong, Hae Kook Lee, Yong-Sil Kwon, Hyeon Woo Yim, Seung-Yup Lee
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences.2020; 31: 69. CrossRef - Prevalence and Interpersonal Correlates of Internet Gaming Disorders among Chinese Adolescents
Xue Yang, Xuewen Jiang, Phoenix Kit-han Mo, Yong Cai, Le Ma, Joseph Tak-fai Lau
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(2): 579. CrossRef - The psychometric properties of the Chinese version internet gaming disorder scale
Wei Lei, Kezhi Liu, Zhen Zeng, Xuemei Liang, Chaohua Huang, Ke Gong, Wenying He, Bo Xiang, Jin Zhang, Xiaojiao Zheng, Jing Chen
Addictive Behaviors.2020; 106: 106392. CrossRef - A partial mediation effect of father-child attachment and self-esteem between parental marital conflict and subsequent features of internet gaming disorder in children: a 12-month follow-up study
Hyunsuk Jeong, Hyeon Woo Yim, Seung-Yup Lee, Hae Kook Lee, Marc N. Potenza, Sun-Jin Jo, Hye Jung Son
BMC Public Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Internet gaming disorder and gaming disorder in the context of seeking and not seeking treatment for video-gaming
Vladan Starcevic, Tae Young Choi, Tae Ho Kim, Seo-Koo Yoo, Sujin Bae, Byung-Sun Choi, Doug Hyun Han
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2020; 129: 31. CrossRef - Examining vulnerability in youth digital information practices scholarship: What are we missing or exhausting?
Mega Subramaniam, Natalie Pang, Shandra Morehouse, S. Nisa Asgarali-Hoffman
Children and Youth Services Review.2020; 116: 105241. CrossRef - Parental and Family Factors Associated with Problematic Gaming and Problematic Internet Use in Adolescents: a Systematic Literature Review
Philip Nielsen, Nicolas Favez, Henk Rigter
Current Addiction Reports.2020; 7(3): 365. CrossRef - Altered Reward Processing System in Internet Gaming Disorder
Syeda Raiha, Guochun Yang, Lingxiao Wang, Weine Dai, Haiyan Wu, Guangteng Meng, Bowei Zhong, Xun Liu
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Conduct problems and depressive symptoms in association with problem gambling and gaming: A systematic review
Jérémie Richard, Émilie Fletcher, Stephanie Boutin, Jeffrey Derevensky, Caroline Temcheff
Journal of Behavioral Addictions.2020; 9(3): 497. CrossRef - Relationships of Internet addiction and Internet gaming disorder symptom severities with probable attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, aggression and negative affect among university students
Cuneyt Evren, Bilge Evren, Ercan Dalbudak, Merve Topcu, Nilay Kutlu
ADHD Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders.2019; 11(4): 413. CrossRef

Figure 1.
| Characteristics | Mean±SD | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 13.0±0.4 | |
| Sex (male) | 223 (55.5) | |
| School type (coeducation) | 4 (100.0) | |
| IGUESS | ||
| 0-5 | 313 (77.8) | |
| 6-9 | 53 (13.2) | |
| ≥10 | 36 (9.0) | |
| AQ | 57.4±15.0 | |
| PACI (father) | 69.8±15.1 | |
| PACI (mother) | 63.0±13.2 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Mean | Standard deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Aggression | 1.00 | 57.34 | 15.00 | |||
| 2. Father-adolescent communication style | -0.22 |
1.00 | 69.80 | 15.06 | ||
| 3. Mother-adolescent communication style | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1.00 | 63.01 | 13.15 | |
| 4. Risk of Internet game disorder | 0.32 |
-0.38 |
-0.05 | 1.00 | 3.61 | 4.00 |
| Aggression | Father-adolescent communication style | Risk of Internet game disorder | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggression | 0.63 | ||
| Father-adolescent communication style | 0.05 | 0.57 | |
| Risk of Internet game disorder | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.65 |
| Index | χ2 | df | χ2/df | GFI | RMSEA | CFI | TLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The mediation model | 201.52 | 87.00 | 2.32 | 0.94 | 0.06 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| Path | Effect |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Direct | Indirect | |
| Aggression → risk of IGD | 0.42 | 0.29 | 0.13 |
SD, standard deviation; IGUESS, Internet Game Use-Elicited Symptom Screen; AQ, Aggression Questionnaire; PACI, Parent-Adolescent Communication Inventory.
Aggression was evaluated by Aggression Questionnaire; Father- and mother-adolescent communication styles were assessed by Parent-Adolescent Communication Inventory; Risk of Internet game disorder was measured by Internet Game Use-Elicited Symptom Screen. p<0.001.
Aggression was evaluated by Aggression Questionnaire; Father- and mother-adolescent communication styles were assessed by Parent- Adolescent Communication Inventory; Risk of Internet game disorder was measured by Internet Game Use-Elicited Symptom Screen.
GFI, goodness of fit index; RMSEA, root mean square error of approximation; CFI, comparative fit index; TLI: Tucker-Lewis index.
GD, Internet game disorder. p <0.001.

 KSE
KSE
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

